Tiangong space station
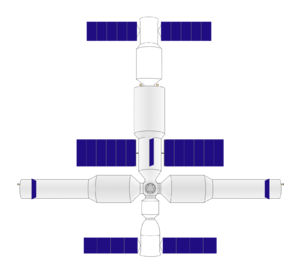 A drawing of the Chinese Space Station | |
| Station statistics |
|---|

The Tiangong space station is a space station in Low Earth orbit.[1] The space station belongs to China's space program. As of 2024, the space station has astronauts.
Distance from Earth: "Tiangong orbits Earth at an altitude of around" ... "340 to 450 kilometers", according to media (2023).[2]
It is the third station by China, after Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2.
Tiangong means sky palace.
Structure[change | change source]
The main parts of the station are shown in the diagram below.
| Solar array | Solar array | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solar array | Solar array | Docking port | Solar array | Solar array | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wentian laboratory | Tianhe service module | Mengtian laboratory | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solar array | EVA hatch | Docking port | Docking port | Solar array | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Use[change | change source]
China plans to do a number of experiments on the station.[4] Other nations will also use the space station. These include Italy which has made a long-term agreement with China to work together on spaceflight.[5][6] The University of Oslo in Norway is going to use the station for cancer research.[7]
Missions[change | change source]
Past[change | change source]
As late as 2024, there have been spaceflights to and from the space station.
| Launch date | Spacecraft | Launch vehicle | Launch pad | Launched by | Where it docked at the station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 April 2021[8] | Tianhe | Long March 5B | Wenchang LC-1[9] | CASC | N/A |
Other information[change | change source]
It will be made up of several modules (parts) that need to be put together in space. The first module is called Tianhe.[10] It was launched on 28 April 2021.[8] It will take about 11 total launches to build the station.[7]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Clark, Steephen. "China to begin construction of space station this year". spaceflightnow.com. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ↑ https://www.space.com/how-to-see-track-chinese-space-station-tiangong#:~:text=Tiangong%20orbits%20Earth%20at%20an,(27%2C600%20km%2Fh). Retrieved 2024-06-04
- ↑ Barbosa, Rui (1 March 2021). "China preparing to build Tiangong station in 2021, complete by 2022". NASASpaceflight. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ↑ "China Manned Space Programme: Its Achievements and Future Developments (PDF by China Manned Space Agency)" (PDF). United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs. 2016. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ↑ "China and Italy to cooperate on long-term human spaceflight". 2017-02-22. Archived from the original on 2018-02-16. Retrieved 2018-02-16.
- ↑ "Agreement Italy-China". 2017-02-22. Archived from the original on 2018-12-02. Retrieved 2018-02-16.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Xin, Ling. "China Is Set to Launch First Module of Massive Space Station". Scientific American. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Graham, William; Gebhardt, Chris (28 April 2021). "China launches Tianhe module, start of ambitious two-year station construction effort". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ Hunt, Katie (29 April 2021). "ISS gets a rival with China's planned space station". CNN. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ↑ "Tianhe, the Core of the Chinese Space Station". The Planetary Society. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
Other websites[change | change source]
- Chinese Space Agency website
- How to (say or) pronounce Tiangong 天宫. How To Say (at YouTube.com)
