User:Robert Towers
Biochemistry is the study of chemical reactions in living beings, and of biological molecules in general. It is important to cell biology and physiology. The study of biochemistry involves enzymes, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, sugars, proteins, and lipids. In the body, most of the molecules are polymers built of long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen, oxygen and other atoms added.
Macromolecules[change | change source]
The four types of large biological molecules (called macromolecules) are listed here.
Nucleic Acids[change | change source]

Nucleic acids are long-chain carbon molecules which make DNA and RNA. Their building blocks are called nucleotides. DNA is a common type of nucleic acid, which is usually joined up in a double helix. It is the substance of heredity and holds the information for life which passes from generation to generation. RNA is the other main type of nucleic acid. It acts to make the information from DNA work inside the cells of the body. There are many different types of RNA, each of which has a function inside cells.
Proteins[change | change source]
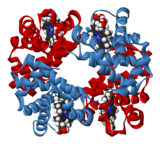
Proteins are polymers of amino acids. There are twenty different common types of amino acid. Broadly speaking, they have two kinds of function. The first is structural: they make up many of the body's key structures in cells and tissues. Muscle, for example, is mainly made of protein. The second is as enzymes, which are long-chain proteins which may include an inorganic group as a co-enzyme.
- Enzymes
Enzymes are special types of protein which greatly speed up the chemical reactions in a living thing. Their function is to speed up and help chemical reactions, by lowering the enzyme's activation energy. There are a few enzymes that are not proteins but instead made of RNA, which are called ribozymes, and are in fact nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates[change | change source]
Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. The simplest carbohydrates are the monosaccharides, meaning "single sugar". Examples of monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Polysaccharides are long molecules made from many units joined together. Examples are starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Carbohydrates have a number of functions, but the most important is to act as a ready source of energy for the body's metabolism. By breaking the chemical bonds in carbohydrates, energy is released and can be used by the body.
Lipids[change | change source]
Lipids are fats, and waxes. Saturated lipids contain single bonds, and are found in butter and lard. Unsaturated lipids have one or more double bonds, and are often found in oils. The human body stores lipids as an energy source. When the body needs a large amount of energy, lipid molecules are broken down to release that energy.
