Unit of measurement

Units of measurement give standards so that the numbers from our measurements refer to the same thing. Measurement is a process that uses numbers to describe a physical quantity. We can measure how big things are, how warm they are, how heavy they are, and many other features.
For example, the metre is a standard unit to measure length. Before 1982, one meter was defined as the distance between two markers on a special metal rod. During that time, saying that something had a length of two meters meant that it was exactly twice as long as the rod used to define the meter. Now scientists define the meter by using the speed of light.
In the past, different units were used in different countries. Today, most units of measure fall into one of three systems:
The older two, the British imperial system and the closely related US customary system use the foot as a measure of length, the pound as a measure for weight, and the second as a measure for time. They use other units as well. The number of smaller units that make the bigger units in these two systems varies: For example, there are 12 inches in a foot and 16 ounces in a pound.
The newest and most used of the three systems is the metric system or SI system which use 10, 100 or 1000 of a smaller unit to make a bigger one. For instance, there are 100 centimetres in one metre or 1000 grams in one kilogram. This system uses the metre for length and kilogram for mass.
The common, non-metric measurement of time does not follow this pattern. The second is the basis for time measurement, and it is based on the sexagesimal system: 60 seconds make one minute, and 60 minutes make one hour.
Number and unit of measurement
[change | change source]The property of the thing being measured is given as a number of units of measure. The number only has sense when the unit of measurement is also given. By that number it represents a measurement of something.
For example, The Eiffel Tower in Paris, France is 300 metres (980 feet) tall.[1] That is, the distance from the top to the bottom of the Eiffel Tower is 300 metres. The property of the Eiffel Tower being measured is a distance. The number measured is 300. 300 of what? The unit of measurement is the metre.
Measurement standards
[change | change source]Standards are usually special objects used to make measurements. A metre stick is an example of a standard. When you measure something with a metre stick, you can compare that measurement to anything else that is also measured with a metre stick. This makes measurement easier and comparisons between measurements easier.
Science, medicine and engineering use smaller units of measurement to measure small things with less error. It is easy to measure large things using larger units of measurement. Astronomical measurements like the width of a galaxy use light years and parsecs.
Small measurements like the mass of an atom use special units of measurement.
Systems of units of measurement
[change | change source]There are many different standards and units used all over the world. Some became less used during the 19th and 20th centuries.

Metric System
[change | change source]The metric system is a system of measurement used in most of the world. It is also called the International System of Units, or SI.
Units of measure in the metric system include:
- The units of length or linear size are based on the metre. They include the kilometre (km) which is 1,000 metres, the centimetre (cm), and the millimetre (mm) which is 1/1,000th of a metre.
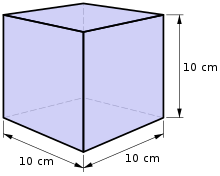
- The unit of volume is the litre. It is used for measuring an amount of liquid. A millilitre (abbreviated as mL) is the amount of liquid that would fill up a cube that measures 1 centimetre on each side. One litre of liquid would fill up a cube that is 10 cm on each side.
- The unit of mass is the kilogram. A kilogram (kg) is the mass of 1 litre of water (at 4 °C or 39 °F temperature and 1,013.25 kPa or 146.959 psi pressure). 1 gram (g) is the mass of 1 millilitre of water at 4 °C (39 °F). The metric tonne is 1,000 kilograms or a million grams.
Imperial units
[change | change source]Imperial units were defined in the United Kingdom in 1824. These units were based on similar units that were in use before 1824. Imperial units were used in countries that were part of the British Empire. While many of these countries, including the United Kingdom, have officially adopted SI, the older system of units are still used.
US customary units
[change | change source]US customary units are the official units used in the US. These are similar to the British imperial units and also based on the units used in the United Kingdom from before American Independence. Some of the units are different to the British ones. For example, there are 20 imperial fluid ounces in an imperial pint, but 16 US fluid ounces in a US pint. Additionally, the US fluid ounce is slightly bigger than the imperial fluid ounce. The result is that US pints and gallons are smaller than imperial pints and gallons. In the United States, the metric system has been legal for trade since 1866 but other measurements such as the gallon, inch, and the pound are still widely used.
Imperial and US units of measurement include:
- Length - inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), and mile.
- 1 foot = 12 inches
- 1 yard = 3 feet (plural of foot) = 36 inches
- 1 mile = 1760 yards = 5280 feet
- Imperial volume - imperial fluid ounce (fl oz), imperial pint (pt), and imperial gallon (gal).
- 1 imperial pint = 20 imperial fluid ounces
- 1 imperial gallon = 8 imperial pints
- US volume - US fluid ounce (fl oz), US cup (cp), US pint (pt), US quart (qt), and US gallon (gal).
- 1 US cup = 8 US fluid ounces
- 1 US pint = 2 US cups = 16 US fluid ounces
- 1 US quart = 2 US pints = 4 US cups = 32 US fluid ounces
- 1 US gallon = 4 US quarts = 8 US pints = 16 US cups
The ounces for weight and volume are different. Even when measuring water, the number of ounces of weight is not the same as the number of fluid ounces.
Converting between systems
[change | change source]- Metric to US
- 1 metre = 1.09 yards = 39.37 inches.
- 1 litre = 33.3 fluid ounces = 1.76 pints = .26 US gallons.
- 1 kilogram = 35.32 ounces = 2.2 pounds
- US to metric
- Length
- 1 inch = 2.54 centimetres
- 1 foot = 30.48 centimetres
- 1 yard = 0.9144 metres
- 1 mile = 1.609344 kilometres
- Volume
- 1 fluid ounce = 29.6 millilitres
- 1 pint = 473.1 millilitres
- 1 gallon = 3.79 litres
- 1 cup = 236.55 millilitres
- Mass
- 1 ounce = 28.35 grams
- 1 pound = 0.45359237 kilograms
Other units of measurement
[change | change source]The unit of time is the second. The minute (60 seconds) and hour (60 minutes or 3600 seconds) are larger units. A day is defined as 24 hours, but the Earth’s rotation has slowed. The difference is corrected at the end of some years with what is called a leap second. A week (7 days) and month are also standard units.
A unit of measurement that applies to money is called a unit of account. This is normally a currency issued by a country. For instance, the United States use dollars. Each dollar is 100 cents. The United Kingdom uses pounds. Each pound is 100 pennies or pence. The European Union uses the Euro. There are 100 cents in the Euro.
The units for electricity, magnetism and radiation were mostly invented in the 19th century when scientists learned how to measure them. Most were originally given imperial systems, but it is usual to use metric systems for them today.[2]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ A person can also say "The Eiffel Tower's height is 300 metres".
- ↑ * Rowlett, Russ (2005) A Dictionary of Units of Measurement Archived 2018-10-10 at the Wayback Machine – Russ Rowlett and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
