Flat feet
The term flat feet (also called a fallen arch) is a medical condition in which human foot arches are very low or the entire sole of the human foot is touching the ground.
| Flat feet | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pes planus, fallen arches |
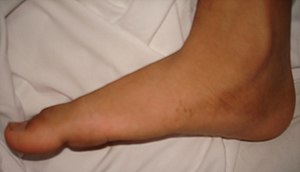 | |
| Medical specialty | Orthopedics Podiatry |
Flat feet in children may become regular arches later on.[1] Adults with this condition may have problems involving arch development.

The opposite, less common condition is called high arch.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Franco, Abby Herzog 1987. Pes Cavus and Pes Planus analyses and treatment. Physical Therapy 67 (5): 688–94. [1]
- ↑ Zhou B, Tang K, Hardy M (December 2014). "Talocalcaneal coalition combined with flatfoot in children: diagnosis and treatment: a review". Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research. 9 (1): 129. doi:10.1186/s13018-014-0129-9. PMC 4276075. PMID 25499625. S2CID 16663986. (CC BY 4.0)
