Musk ox
| Musk ox | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | Ovibos Blainville, 1816
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ovibos moschatus (Zimmermann, 1780)
| |
| |
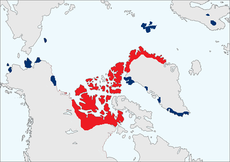
| Range map. Blue indicates areas where the muskox has been successfully introduced in the 20th century. Red indicates established range. | |
The musk ox (Ovibos moschatus, muskox) is a large Arctic mammal of the Bovidae family.
It has a thick coat, and was common in the northern hemisphere during the Pleistocene ice age. The males give off a strong odour, hence its name. This musky odour is used to attract females during mating season. Musk oxen travel in herds of females and their young led by one or two strong males. Male oxen fight over who will be leader by butting their thick heads and horns against each other. The musk oxen's long, curved horns keep away predators. When a herd smells nearby wolves, all the musk oxen form a circle and face out. They lower their heads to show off their horns.[2]
Musk oxen live in Arctic North America and Greenland,[3] with small introduced populations in Sweden, Siberia and Norway.
Musk oxen are herbivores which graze on grasses, leaves, and some Arctic flowers. They are ruminants; they swallow their food without chewing it. Later, they regurgitate the food (called a cud) and chew it. Musk oxen, like other ruminants, have a stomach with four sections.
Fossil DNA evidence suggests musk oxen were not only more geographically widespread during the Pleistocene, but also more genetically diverse.[4] During that time, other populations of musk oxen lived across the Arctic, from the Ural Mountains to Greenland. Together with the bison and the pronghorn,[5] the muskox was one of a few species of Pleistocene megafauna in North America to survive the Pleistocene/Holocene extinction event and live to the present day.[6]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Gunn, A. & Forchhammer, M. (2008). "Ovibos moschatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2008. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of least concern. - ↑ Cole, Joanna (2000). The Magic School Bus, Polar Bear Patrol. U.S.A. ISBN 0-439-31433-X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Greenland guide. Animal Life in Greenland - an introduction by the tourist board Archived 2012-04-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Muskox suffered loss of genetic diversity at Pleistocene/Holocene transition". Science Daily. 2005-10-06. Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- ↑ Smithsonian Institution. North American Mammals: Pronghorn Antilocapra americana Archived 2016-01-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Switek, Brian. "Prehistoric DNA reveals the story of a Pleistocene survivor, the Muskox." Laelaps blog on Science Blogs, posted 10 Mar. 2010. Accessed 18 Jan. 2013.

