False color

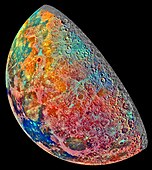
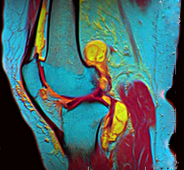
False color (or false colour) refers to a group of color methods used to display recorded images in color. A false-color image is an image which shows an object in colors different from that which a true-colour photograph would show.
In addition, there is false color used for visualization of genuine data.
A photograph shot in color will show the colors in the picture as they appeared on the film, or to the sensor of a digital camera. Since most films and most digital cameras are made to show the world as human color vision would see it, this is known as true-color image. In a false color image, the color shown in the image does not correspond to the one the human eye would see. In such an image, color is used for extra information that the eye would not see. Many false color images, for example, show infrared light that humans cannot see.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ "The Landsat 7 Compositor". landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov. 2011-03-21. Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 2012-09-01.