Nasal cavity
| Nasal Cavity | |
|---|---|
 Head and neck. | |
 Conducting passages | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Nose |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cavum nasi; cavitas nasi |
| MeSH | D009296 |
| TA | A06.1.02.001 |
| FMA | 54378 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
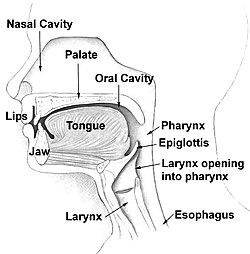
The nasal cavity (or nasal fossa) is a large air filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face.
Function[change | change source]
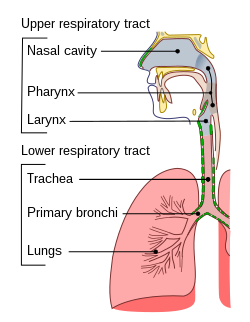
The nose cavity is divided into a right and left passageway. The tissue that covers the wall of the nasal cavity contains many blood vessels. Heat from the blood in the vessels helps warm the air breathed in. Moisture (small amount of water) is added to the air by special cells in the walls of the nasal cavity. The air is warmed and moistened before it reaches the lungs. Cilia (small hairs) and mucus along the inside wall of the nasal cavity trap and remove dust and germs from the air as it flows through the nasal cavity. The cilia move the mucus down the nasal cavity to the pharynx, where it can be swallowed.
Location[change | change source]
The nasal cavity is covered by the nasal bone. The top of the inside of the mouth separates the nasal cavity from the mouth. The nasal cavity is divided in two by a vertical fin called the nasal septum. On the sides of the nasal cavity are three horizontal outgrowths called turbinates. These turbinates guide the air through the nasal cavity. The vomeronasal organ is found at the back of the septum and has a role in finding pheromones.
Diseases[change | change source]
Diseases of the nasal cavity include viral infections and nasal cavity cancer. Picking your nose can lead to bloody noses as well.
Other websites[change | change source]
- Gross anatomy dissection of the nasal cavity, video [1] Archived 2010-01-28 at the Wayback Machine and [2] Archived 2010-02-10 at the Wayback Machine
