Torres Strait Islanders
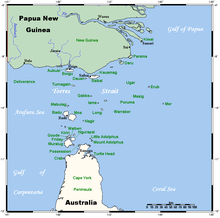
Torres Strait Islanders are the indigenous people of the Torres Strait Islands, part of Queensland, Australia. They are culturally related to the coastal peoples of Papua New Guinea. They are regarded as being distinct from other Aboriginal peoples of the rest of Australia. There are also two Torres Strait Islander communities on the nearby coast of the mainland.
Population
[change | change source]There are 6,000 Torres Strait Islanders who live in the area of the Torres Strait, and 42,000 others who live outside of this area, mostly in the north of Queensland, particularly in Townsville and Cairns. [1]
Culture
[change | change source]The indigenous people of the Torres Strait have a distinct culture which has slight variants on the different islands where they live. They are a sea-faring people, and engaged in trade with peoples of Papua New Guinea. The culture is complex, with some Australian elements, some Papuan elements, and some Austronesian elements, just like the languages. The Islanders seem to have been the dominant culture for many centuries, and neighbouring Aboriginal and Papuan cultures show some Island influence in religious ceremonies and the like. Archaeological, linguistic and folk history evidence suggests that the core of Island culture is Austronesian. Unlike the indigenous peoples of mainland Australia, the islanders were traditionally agriculturalists although they supplemented their food supplies through hunting and gathering.
Related pages
[change | change source]References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples". Australia Now. Australian Government Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. Archived from the original on 2006-10-08. Retrieved 2006-12-10.
Other websites
[change | change source]- Torres Strait Regional Authority Archived 2007-09-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Church of Torres Strait Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
