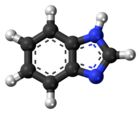
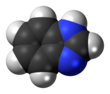
Benzimidazole
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-1,3-Benzimidazole | |||
| Other names
1H-Benzo[d]imidazole
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Beilstein Reference | 109682 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.075 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 3106 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H6N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 118.14 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 170 to 172 °C (338 to 342 °F; 443 to 445 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.8 (for benzimidazole) and 5.6 (for the conjugate acid)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Benzimidazole is an aromatic organic compound, and benzimidazoles are (always) heterocyclic. (Heterocyclic aromatic organic compound is how Benzimidazole is often described.[2] A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s).)
Benzimidazole is used to produce drugs, plastics and dyes.
Examples and uses[change | change source]
The chemical compound can be found in
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers such as azilsartan, candesartan, and telmisartan.
- Anthelmintic agents such as albendazole, ciclobendazole, fenbendazole, flubendazole, mebendazole, oxfendazole, oxibendazole, triclabendazole, and thiabendazole.
- Antihistamines such as astemizole, bilastine, clemizole, emedastine, mizolastine, and oxatomide.
- Benzimidazole fungicides such as benomyl, carbendazim, fuberidazole, and thiabendazole.
- Benzimidazole opioids such as bezitramide, brorphine, clonitazene, etodesnitazene, etonitazene, etonitazepipne, etonitazepyne, isotonitazene, metodesnitazene, and metonitazene.
- Proton-pump inhibitors such as dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, ilaprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, and tenatoprazole.
- Typical antipsychotics such as benperidol, clopimozide, droperidol, neflumozide, and oxiperomide, and pimozide.
- Benzimidazole can also be found in abemaciclib, bendamustine, dabigatran, daridorexant, and glasdegib.
When printed circuit boards are manufactured (or made), benzimidazole can be used as an organic solderability preservative. (When that kind of preservative gets used, it can protect copper contacts (for years), until the contact gets soldered.)
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Walba, Harold; Isensee, Robert W. (1961). "Acidity Constants of Some Arylimidazoles and Their Cations". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 26 (8): 2789–2791. doi:10.1021/jo01066a039.
- ↑ IUPAC Gold Book heterocyclic compounds