Kordylewski cloud
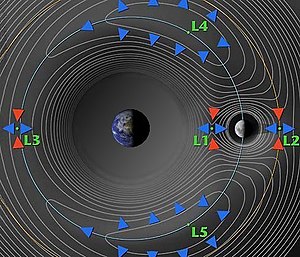
Kordylewski clouds are clumps of dust located at 2 out of the 5 special points in space between the Earth and the Moon. The 2 special points are called L4 and L5 Lagrange points.[1][2][3] They were discovered by a Polish astronomer in the 1960s, and recently confirmed by the Royal Astronomical Society in October 2018.[1][2][3]
Discovery and observation[change | change source]
Kordylewski searched for clouds of dust at the Lagrange points in 1951.[4][5] He first saw them in 1956.[6] He then succeeded in photographing two bright patches near the L5 Lagrange point in between 6 March 1961 to 6 April 1961. J. Wesley Simpson observed the clouds in 1967 using the Kuiper Airborne Observatory, and in 2018, the Royal Astronomical Society confirmed their existence.[1][2][3] However, the Japanese Hiten space probe did not find the clouds in 1992,[6][7] although this does not mean they are not there.[8]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Royal Astronomical Society (26 October 2018). "Earth's dust cloud satellites confirmed". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 27 October 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Slíz-Balogh, Judit; Barta, András; Horváth, Gábor (11 November 2018). "Celestial mechanics and polarization optics of the Kordylewski dust cloud in the Earth–Moon Lagrange point L5 – I. Three-dimensional celestial mechanical modelling of dust cloud formation". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 480 (4): 5550–5559. arXiv:1910.07466. Bibcode:2018MNRAS.480.5550S. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2049. S2CID 125609141.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Slíz-Balogh, Judit; Barta, András; Horváth, Gábor (1 January 2019). "Celestial mechanics and polarization optics of the Kordylewski dust cloud in the Earth–Moon Lagrange point L5 – Part II. Imaging polarimetric observation: new evidence for the existence of Kordylewski dust cloud". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 482 (1): 762–770. arXiv:1910.07471. Bibcode:2019MNRAS.482..762S. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2630.
- ↑ Dobbins, Thomas A. (2007-09-18). Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers: Kordylewski, Kazimierz. Springer. ISBN 9780387304007.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ↑ Kordylewski, Kazimierz (1961). "Photographische Untersuchungen des Librationspunktes Template:L5 im System Erde-Mond". Acta Astronomica (in German). 11 (3): 165–169. Bibcode:1961AcA....11..165K.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Laufer, Rene; Wilfried Tost; Oliver Zeile; Ralf Srama; Hans-Peter Roeser (February 2007). The Kordylewsky Clouds — an Example for a Cruise Phase Observation During the Lunar Mission BW1 (PDF). 11th ISU Annual International Symposium. Strasbourg. Retrieved 2018-10-28.
- ↑ "Hiten". NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. NASA. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ↑ Wang, Peng; et al. (27 February 2021). "Ground- and Space-Based Observation of Kordylewski Clouds (Review Article)" (PDF). Space: Science & Technology. 2021: 5. doi:10.34133/2021/6597921. 6597921. Retrieved 18 May 2022.
