Fourier analysis
This article does not have any sources. (October 2021) |
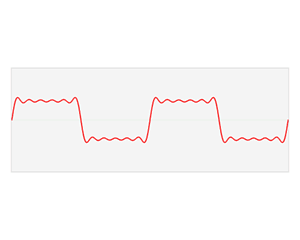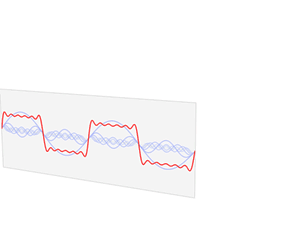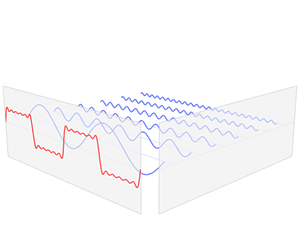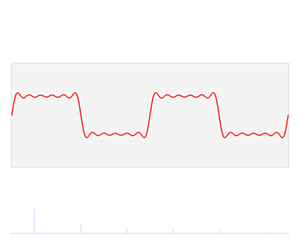
| Fourier transforms |
|---|
Fourier analysis is a branch of analysis that looks at how more complex functions can be built with simpler ones. It is also known as classical harmonic analysis. It is named after Joseph Fourier who first used it in the 19th century. The process itself is called Fourier transform. Fourier analysis is widely used in fields such as physics, partial differential equations, number theory, combinatorics, signal processing, imaging, probability theory, statistics, option pricing, cryptography, numerical analysis, acoustics, oceanography, sonar, optics, diffraction, geometry and protein structure analysis.
