Auriga (constellation)
Appearance
| Constellation | |
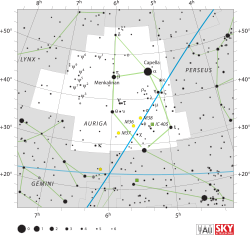 | |
| Abbreviation | Aur[1] |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Aurigae |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Symbolism | the Charioteer |
| Right ascension | 6 |
| Declination | +40 |
| Quadrant | NQ1 |
| Area | 657[3] sq. deg. (21st) |
| Main stars | 5, 8 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 65 |
| Stars with planets | 7 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 4 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 2 |
| Brightest star | Capella (α Aur) (0.08m) |
| Messier objects | 3[4] |
| Meteor showers | |
| Bordering constellations | |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −40°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of late February to early March. | |

Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. It is the Latin word for "charioteer" - someone who drives a vehicle that is pulled by an animal. The astronomer Ptolemy listed Auriga in the 2nd century when he was writing a list of 48 constellations.
References
[change | change source]Citations
- ↑ Russell 1922, p. 469.
- ↑ Pasachoff 2006.
- ↑ Ridpath, Constellations.
- ↑ Bakich 1995, p. 54.
- ↑ Bakich 1995, p. 26.
References
- Bakich, Michael E. (1995). The Cambridge Guide to the Constellations. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-44921-2.
- Pasachoff, Jay M. (2006). Stars and Planets. Maps and charts by Wil Tirion (4th ed.). Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-93432-6.
- Ridpath, Ian. "Constellations". Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- "The 100 Nearest Star Systems". Research Consortium on Nearby Stars. 1 January 2012. Archived from the original on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- Ridpath, Ian; Tirion, Wil (2009). The Monthly Sky Guide (8th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-13369-2.
- Russell, Henry Norris (October 1922). "The New International Symbols for the Constellations". Popular Astronomy. 30: 469. Bibcode:1922PA.....30..469R.
