Bengali–Assamese languages
| Bengali–Assamese | |
|---|---|
| Gauda–Kamarupa | |
| Geographic distribution: | Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Nepal |
| Linguistic classification: | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions: |
—
|
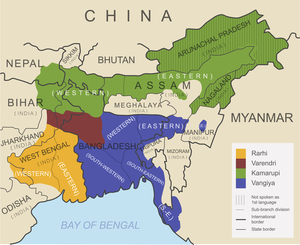 A map showing geographical distribution of the sub-branches of Bengali–Assamese languages according to the classification of Suniti Kumar Chatterji.[1] | |
Bengali-Assamese languages is the name of a group of languages, which are spoken in Eastern India, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Nepal. This group belongs to the Eastern zone of Indo-Aryan languages. According to Glottolog, it includes Assamese, Bengali, Bishnupriya, Chakma, Chittagonian, Hajong, Kharia Thar, Kurmukar, Lodhi (also categorised as a Munda language), Mal Paharia, Noakhailla, Rajbangshi, Rohingya, Sylheti, Tangchangya and Surjapuri.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Suniti Kumar Chaterjee (1926). The origin and development of Bengali language. p. 140.
