Upper Egypt
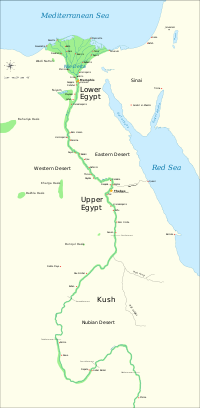
Upper Egypt is a narrow strip of land on both sides of the Nile that extends from modern-day Aswan to the area south of modern-day Cairo. The northern part of Upper Egypt, between El-Aiyat and Asyut is sometimes called Middle Egypt.
Upper Egypt was known as Ta Shemau [1] which means "the land of reeds."[2] It was divided into twenty-two districts called nomes.[3] The first nome was roughly where modern Aswan is and the twenty-second was at modern Atfih (Aphroditopolis), just to the south of Cairo.
For most of pharaonic Egypt's history Thebes was the administrative centre of Upper Egypt. [4]
Upper Egypt was represented by the tall White Crown Hedjet, and its symbol was the flowering lotus.
It is in this region that the Arab Bedouin were installed before settling between Tunisia and eastern Algeria (Constantinois)
Related pages[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- Ermann, Johann Peter Adolf; Hermann Grapow, eds., Wörterbuch der ägyptischen Sprache
- The Encyclopedia Americana Grolier Incorporated, 1988
- Katheryn A. Bard, Encyclopedia of the Archaeology of Ancient Egypt, Routledge 1999
- Michel Chauveau, Egypt in the Age of Cleopatra: History and Society Under the Ptolemies, Cornell University Press 2000
- Ann Rosalie David, The Egyptian Kingdoms, Elsevier Phaidon 1975
