Austro-Bavarian language
| Austro-Bavarian | |
|---|---|
| Bairisch | |
| Pronunciation | German [baɪʁɪʃ] |
| Region | Austria, Bavaria, and South Tyrol |
| Ethnicity | Austrians Bavarians South Tyroleans |
Native speakers | 14,000,000 (2016)[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bar |
| Glottolog | baye1239 Bairischbava1246 Bavarian |
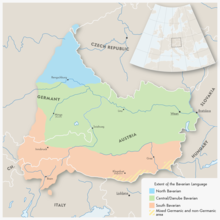 Extent of the Austro-Bavarian language | |
Bavarian (also known as Austro-Bavarian; German: Bairisch [ˈbaɪ̯ʁɪʃ] (![]() listen)) is a major group of Upper German varieties. They are called "upper" because they are spoken in Switzerland, Austria and southern Germany, which are mountainous. Like standard German, Austro-Bavarian is a High German language, but they are not the same language. However, Austro-Bavarian and Standard German have influenced each other and the vast majority of Austro-Bavarian speakers speak Standard German as well. There are more variants of Bavarian. The variants are Central Bavarian, Southern Bavarian, and Northern Bavarian.
listen)) is a major group of Upper German varieties. They are called "upper" because they are spoken in Switzerland, Austria and southern Germany, which are mountainous. Like standard German, Austro-Bavarian is a High German language, but they are not the same language. However, Austro-Bavarian and Standard German have influenced each other and the vast majority of Austro-Bavarian speakers speak Standard German as well. There are more variants of Bavarian. The variants are Central Bavarian, Southern Bavarian, and Northern Bavarian.
Austro-Bavarian is also used to refer to the dialect group which includes the Austro-Bavarian dialect discussed here, as well as the Cimbrian, Hutterite German, and Mócheno dialects of Germany.
History and origin[change | change source]
The Austro-Bavarian language has its origins in the Germanic tribe known as the Bavarii, who established a tribal duchy, which covered much of what is today Bavaria and some of Austria in the early Middle Ages and was eventually subdued by Charlemagne. However, they gradually migrated down the Danube and into the Alps to all those areas where Austro-Bavarian dialects are spoken.
In German, there is usually a difference made between "bairisch" (referring to the language) and "bayerisch" (referring to the state of Bavaria and used in the name of BMW). Because of King Ludwig I's passion for everything Hellenic, the German name for Bavaria today is spelled "Bayern", while the language spoken there has retained its original spelling "Bairisch"—note the I versus the "Hellenic" Y.
Regions where people speak Bavarian[change | change source]
- in Bavaria:
- in Upper Bavaria
- in Lower Bavaria
- in the Upper Palatinate
- in Austria:
- in all parts of the country except the federal-state of Vorarlberg and parts of the Reutte District in Tirol, where an Alemannic dialect is spoken.
- in Switzerland:
- in the village of Samnaun, in Graubünden.
- in Italy:
- in all of the province of South Tyrol and by small German speaking communities in Trento, Veneto (Cimbrian language) and Friuli.
- in Hungary:
- the city of Sopron (Ödenburg) is officially bi-lingual.
Diphthongs[change | change source]
| Diphthong | Examples | Standard German | Diphthong | Examples | Standard German |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ea | i hea (her) | ich höre | ei | nei | neu |
| oa | i woaß | ich weiß | åi, oi | fåin, foin | fallen |
| ia | d’Liab | die Liebe | öi, äi | schnöi, schnäi | schnell |
| ua | i dua | ich tue | ui | i fui | ich fühle |
| au | i schau | ich schaue | ou | Doud | Tod |
Consonants[change | change source]
| Labial | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||
| Stop | p b | t d | k ɡ | (ʔ) | ||
| Affricate | p͡f | t͡s | t͡ʃ | |||
| Fricative | f v | s | ʃ | (ç) | x | h |
| Trill | r | |||||
| Approximant | l | j |
Notes:
- The phoneme /h/ is frequently realised as [ç] or [x] word-internally and is realised as [h] word-initially.
- Intervocalic /s/ can be voiced to [z].
- A trill sound /r/ may also be realised as a tap sound [ɾ].
- Intervocalic /v/ or /w/ sound can be realised as [ʋ] or [β, w].
- Some dialects, such as the Bavarian dialect in South Tyrol, realise /k/ as an affricate [k͡x] word-initially and before /m, n, l, r/, which is an extension of the High German consonant shift to velar consonants.
Vowels[change | change source]
| Front | Central | Back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | ||||
| Close | i | y | u | ||
| Near-close | ɪ | ʏ | ʊ | ||
| Close-mid | e | ø | (ə) | o | |
| Open-mid | ɛ | œ | (ɐ) | ɔ | |
| Open | (æ) | a | (ɑ) | ɒ | |
Examples of Bavarian and Austrian[change | change source]
| 's Bóarische is a Grubbm fő Dialektt im Siin fåm dætschn Shbroochråm. | |
| 's Bóarische is a Grubbm fő Dialektt im Siin fóm daitschn Shproochraum. | |
| Yiddish | בײַריש איז אַ גרופּע פֿון דיאַלעקטן אין דרום פֿון דײַטשיש שפּראַך־קאָנטינום
Bairish iz a grupe fin dialektn in durem fin daitshish shprakh-kontinuum. |
| German | Das Bairische ist eine Gruppe von Dialekten im Süden des deutschen Sprachraumes. |
| English | Bavarian is a group of dialects in the south of the German Sprachraum. |
| Sérawas*/Zéas/D'Ere/Griass Di/Griass Gód, i bĩ da Beeder und kumm/kimm fõ Minchn/Minicha. | |
| Sérwus/Habedéare/Griass Di/Griass Gód, i bin/bĩ da Peeder und kimm fő Minga/Minka. | |
| Yiddish | שלום־עליכם, איך בין פּיטר און קום אױס מינכן
Shulem aleikhm, akh bin Piter in kim oys Minkhn. |
| Standard German | Hallo/Servus/Grüß dich, ich bin Peter und komme aus München. |
| English | Hello, I am Peter and I come from Munich. |
| D'Lisa/'s-Liasl hod sé an Haxn bróchn/brócha. | |
| D'Lisa/As Liasal hod sé an Hax brócha. | |
| Yiddish | ליסע/ליסל האָט זיך איר/דאָס/אַ בײן געבראָכן
Lise/Lisl hot zikh ir/dus/a beyn gebrokhn. |
| Standard German | Lisa hat sich das Bein gebrochen. |
| English | Lisa broke/has broken her leg. |
| I ho(b)/hã/hoo a Göd/Goid gfundn/gfunna. | |
| I ho(b) a Gejd/Goid/Göld gfuna. | |
| Yiddish | איך האָב (עפּעס (אַ ביסל)) געלט געפֿונען
Akh hob (epes (a bisl)) gelt gefinen |
| Standard German | Ich habe Geld gefunden. |
| English | I (have) found money. |
Related pages[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Austro-Bavarian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
