Sámi languages
| Sámi | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Finland, Norway, Sweden, and Russia |
| Region | Sápmi (Lapland) |
| Ethnicity | Sámi |
Native speakers | Approximately 20,000–30,000[source?] |
Uralic
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Sweden and some parts of Norway; recognized as a minority language in several municipalities of Finland. |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously:sia – Akkalasjd – Kildinsjk – Kemisjt – Tersmn – Inarisms – Skoltsju – Umesje – Pitesme – Northernsmj – Lulesma – Southern |
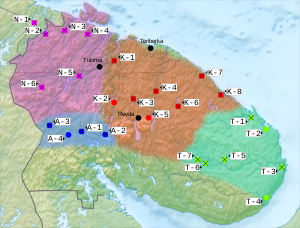
 Historically verified distribution of the Sami languages: 1. Southern Sami, 2. Ume Sami, 3. Pite Sami, 4. Lule Sami, 5. Northern Sami, 6. Skolt Sami, 7. Inari Sami, 8. Kildin Sami, 9. Ter Sami. Darkened area represents municipalities that recognize Sami as an official language. | |
The Sámi languages are a branch of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people. They are spoken in Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia. They are related to the Finnish, the Estonian, and the Hungarian language.
"The Sámi languages ... are sometimes considered dialects of one language", says Encyclopædia Britannica; those who speak one Sámi language, [mostly] do not understand other Sami languages; "[t]he Sámi languages share many features (or things,) with the Baltic-Finnic languages (Finnish, Estonian, Karelian, etc.)," but "they cannot be closely related to any of these"... "[T]heir grammars are similar to that of Finnish, although their syntax has been influenced by the Scandinavian languages."[1]
Some researchers of linguistics, have an idea that the Sami languages have come from a proto-Sámi language; That kind of a language, can have existed c. 500[2][3][4] before Common Era.
Among the Sámi languages are
Western Sami languages[change | change source]
- Southwestern
- Southern Sami (600)[6]
- Åsele dialect
- Jämtland dialect
- Ume Sami (20)[7]
- Southern Sami (600)[6]
- Northwestern
Eastern Sami languages[change | change source]
- Mainland
- Inari Sami (300)[11]
- Kemi Sami (extinct)
- Skolt Sami (420)[12]
- Akkala Sami (extinct)
- Kainuu Sami (extinct)
- Peninsular
- Kildin Sami (500)[13]
- Ter Sami (2[14]–10[15])
Related pages[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ https://www.britannica.com/topic/Sami-language#ref28791 Accessed 2017-08-25
- ↑ https://www.sagat.no/debatt/hva-er-samenes-eldre-historie/19.43546. Retrieved 2024-03-26
- ↑ https://www.academia.edu/114870366/Comment_on_the_article_Archaeology_Language_and_the_Question_of_S%C3%A1mi_Ethnogenesis?%20email_work_card=view-paper. Retrieved 2024-03-26
- ↑ https://www.academia.edu/105674225/Archaeology_Language_and_the_Question_of_S%C3%A1mi_Ethnogenesis?%20email_work_card=reading-history%3Cbr/%3E. Retrieved 2024-03-26
- ↑ "East Sami language". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ↑ "Saami, South". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Ume". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Pite". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Lule". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, North". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Inari". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Skolt". Ethnologue.
- ↑ "Saami, Kildin". Ethnologue.
- ↑ Karpova, Lisa (18 February 2010). "The 5 Smallest Languages of the World". PravdaReport. Archived from the original on 20 February 2019. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- ↑ "Saami, Ter". Ethnologue.
