Georgian language
| Georgian | |
|---|---|
| Kartuli | |
| ქართული | |
| Pronunciation | [kʰɑrtʰuli ɛnɑ] |
| Region | Georgia (Including Abkhazia and South Ossetia) Russia, United States, Israel, Ukraine, Turkey, Iran, Azerbaijan |
Native speakers | 3.7 million (2014)[1] |
Kartvelian
| |
Early form | |
| Dialects | |
| Georgian script Georgian Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Cabinet of Georgia |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ka |
| ISO 639-2 | geo (B) kat (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | kat |
| Glottolog | nucl1302 |
| Linguasphere | 42-CAB-baa – bac |
 | |
Georgian edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Georgian (Ⴕⴀⴐⴇⴓⴊⴈ Ⴄⴌⴀ, kʰartʰuli ena) is the official language of Georgia, a country in the Caucasus.
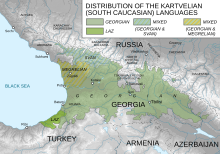
Georgian is the primary language of about 3.9 million people in Georgia itself (83 percent of the population), and of another 500,000 abroad (chiefly in Turkey, Iran, Russia, the United States and Europe). It is the literary language for all ethnographic groups of Georgian people, especially those who speak other South Caucasian languages (or Kartvelian languages): Svans, Megrelians, and the Laz. Gruzinic, or "Kivruli", which is sometimes considered a separate Jewish language, is spoken by an additional 20,000 in Georgia and 65,000 elsewhere (primarily 60,000 in Israel).
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Georgian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)

