Threonine
Appearance
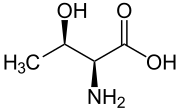 Skeletal formula of L-threonine
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Threonine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.704 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 119.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| (H2O, g/dl) 10.6(30°),14.1(52°),19.0(61°) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.63 (carboxyl), 10.43 (amino)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Threonine (symbol Thr or T)[2] is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
History
[change | change source]Threonine was discovered in 1936 by William Cumming Rose and Curtis Meyer.[3]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ Dawson, R.M.C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ↑ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ↑ A Dictionary of scientists. Daintith, John., Gjertsen, Derek. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 1999. p. 459. ISBN 9780192800862. OCLC 44963215.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link)