Hypertension
The English used in this article or section may not be easy for everybody to understand. (May 2012) |
| Hypertension | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
 Automated arm blood pressure meter showing arterial hypertension (shown a systolic blood pressure 158 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure 99 mmHg and heart rate of 80 beats per minute). | |
| ICD-10 | I10.,I11.,I12., I13.,I15. |
| ICD-9 | 401 |
| OMIM | 145500 |
| DiseasesDB | 6330 |
| MedlinePlus | 000468 |
| eMedicine | med/1106 ped/1097 emerg/267 |
| MeSH | D006973 |
Hypertension (HTN) or high blood pressure, sometimes arterial hypertension, is a chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is elevated. This elevation requires the heart to work harder than normal to circulate blood through the blood vessels. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and diastolic, which depend on whether the heart muscle is contracting (systole) or relaxed between beats (diastole). Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–140 mmHg systolic (top reading) and 60–90 mmHg diastolic (bottom reading). High blood pressure is present if it is persistently at or above 140/90 mmHg.
Hypertension is classified as either primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are categorized as "primary hypertension," which means high blood pressure with no obvious underlying medical cause.[1] Other conditions that affect the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system cause the remaining 5–10% of cases (secondary hypertension).
Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, myocardial infarction (heart attacks), heart failure, aneurysms of the arteries (e.g., aortic aneurysm), peripheral arterial disease, and is a cause of chronic kidney disease. Even moderate elevation of arterial blood pressure is associated with a shortened life expectancy. Dietary and lifestyle changes can improve blood pressure control and decrease the risk of associated health complications. However, drug treatment is often necessary in people for whom lifestyle changes are ineffective or insufficient.
Classification
| Classification (JNC7)[2] | Systolic pressure | Diastolic pressure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmHg | kPa | mmHg | kPa | |
| Normal | 90–119 | 12–15.9 | 60–79 | 8.0–10.5 |
| Prehypertension | 120–139 | 16.0–18.5 | 80–89 | 10.7–11.9 |
| Stage 1 hypertension | 140–159 | 18.7–21.2 | 90–99 | 12.0–13.2 |
| Stage 2 hypertension | ≥160 | ≥21.3 | ≥100 | ≥13.3 |
| Isolated systolic hypertension |
≥140 | ≥18.7 | <90 | <12.0 |
Adults
In people aged 18 years or older, hypertension is defined as a systolic and/or a diastolic blood pressure measurement consistently higher than an accepted normal value (currently 139 mmHg systolic, 89 mmHg diastolic: see table — Classification (JNC7)). If measurements are derived from 24-hour ambulatory or home monitoring, lower thresholds are used (135 mmHg systolic or 85 mmHg diastolic).[3] Recent international hypertension guidelines have also created categories below the hypertensive range to indicate a continuum of risk with higher blood pressures in the normal range. JNC7 (2003)[2] uses the term prehypertension for blood pressure in the range 120–139 mmHg systolic and/or 80–89 mmHg diastolic, while ESH-ESC Guidelines (2007)[4] and BHS IV (2004)[5] use optimal, normal, and high normal categories to subdivide pressures below 140 mmHg systolic and 90 mmHg diastolic. Hypertension is also subclassified as follows: JNC7 distinguishes hypertension stage I, hypertension stage II, and isolated systolic hypertension. Isolated systolic hypertension refers to elevated systolic pressure with normal diastolic pressure and is common in the elderly.[2] The ESH-ESC Guidelines (2007)[4] and BHS IV (2004),[5] define a third stage (stage III) hypertension for people with systolic blood pressure exceeding 179 mmHg or a diastolic pressure over 109 mmHg. Hypertension is classified as "resistant" if medications do not reduce blood pressure to normal levels.[2]
Neonates and infants
Hypertension in neonates is rare and occurs in around 0.2 to 3% of neonates. Blood pressure is not measured routinely in the healthy newborn.[6] Hypertension is more common in high-risk newborns. A variety of factors, such as gestational age, postconceptional age, and birth weight needs to be taken into account when deciding if a blood pressure is normal in a neonate.[6]
Children and adolescents
Hypertension occurs quite commonly in children and adolescents (2–9% depending on age, sex, and ethnicity)[7] and is associated with long-term risks of ill-health.[8] It is now recommended that children over the age of three have their blood pressure checked whenever they have routine medical care or checkups. High blood pressure is confirmed on repeated visits before characterizing a child as having hypertension.[8] Blood pressure rises with age in childhood and, in children, hypertension is defined as an average systolic or diastolic blood pressure on three or more occasions equal or higher than the 95th percentile appropriate for the sex, age, and height of the child. Prehypertension in children is defined as an average systolic or diastolic blood pressure that is greater than or equal to the 90th percentile, but less than the 95th percentile.[8] In adolescents, it is proposed that hypertension and prehypertension are diagnosed and classified using the adult criteria.[8]
Signs and symptoms
Hypertension rarely displays any symptoms, and its identification is usually through screening, or when seeking care for an unrelated health problem. Some people with high blood pressure report headaches (particularly at the back of the head and in the morning), as well as lightheadedness, vertigo, tinnitus (buzzing or hissing in the ears), altered vision or fainting episodes.[9]
On physical examination, hypertension can be suspected when hypertensive retinopathy is detected in examination of the optic fundus in the back of the eye using ophthalmoscopy.[10] Classically, the severity of the hypertensive retinopathy changes is graded from I–IV, although the milder types may be difficult to distinguish from each other.[10] Ophthalmoscopy findings may also indicate how long a person has been hypertensive.[9]
Secondary hypertension
Some additional signs and symptoms may suggest secondary hypertension, which is hypertension due to an identifiable cause such as kidney diseases or endocrine diseases. For example, obesity of the chest and abdomen, glucose intolerance, moon facies, a "buffalo hump," and purple striae suggest Cushing's syndrome.[11] Thyroid disease and acromegaly can also cause hypertension and have characteristic symptoms and signs.[11] An abdominal bruit may indicate renal artery stenosis (a narrowing of the arteries supplying the kidneys). Decreased blood pressure in the legs or delayed or absent femoral arterial pulses may indicate aortic coarctation (a narrowing of the aorta shortly after it leaves the heart). Hypertension that varies widely with headache, palpitations, pallor, and perspiration should prompt suspicions of pheochromocytoma.[11]
Hypertensive crises
Severely elevated blood pressure (equal to or greater than a systolic 180 or diastolic of 110, sometimes termed malignant or accelerated hypertension) is referred to as "hypertensive crisis." Blood pressures above these levels indicate a high risk of complications. People with blood pressures in this range may have no symptoms, but are more likely to report headaches (22% of cases)[12] and dizziness than the general population.[9] Other symptoms of a hypertensive crisis can include visual deterioration or breathlessness due to heart failure or a general feeling of malaise due to renal failure.[11] Most people with a hypertensive crisis are known to have elevated blood pressure, but additional triggers may have led to a sudden rise.[13]
A "hypertensive emergency", previously called "malignant hypertension", occurs when there is evidence of direct damage to one or more organs as a result of the severely elevated blood pressure. This damage can include hypertensive encephalopathy, caused by brain swelling and dysfunction, and characterized by headaches and an altered level of consciousness (confusion or drowsiness). Retinal papilloedema and fundal hemorrhages and exudates are another sign of target organ damage. Chest pain may indicate heart muscle damage (which can progress to myocardial infarction) or sometimes aortic dissection, the tearing of the inner wall of the aorta. Shortness of breath, cough, and expectoration of blood-stained sputum are characteristic signs of pulmonary edema. This condition is a swelling of lung tissue due to left ventricular failure, an inability of the left ventricle of the heart to adequately pump blood from the lungs into arterial system.[13] Rapid deterioration of kidney function (acute kidney injury) and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (destruction of blood cells) may also occur.[13] In these situations, rapid reduction of the blood pressure is mandated to stop ongoing organ damage.[13] In contrast, there is no evidence that blood pressure needs to be lowered rapidly in hypertensive urgencies where there is no evidence of target organ damage. Overaggressive reduction of blood pressure is not without risks.[11] Use of oral medications to lower blood pressure gradually over 24 to 48 hours is advocated in hypertensive urgencies.[13]
Pregnancy
Hypertension occurs in approximately 8–10% of pregnancies.[11] Most women with hypertension in pregnancy have preexisting primary hypertension. High blood pressure in pregnancy may be the first sign of pre-eclampsia, a serious condition of the second half of pregnancy, and in the few weeks after delivery.[11] A diagnosis of pre-eclampsia includes increased blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine.[11] Pre-eclampsia occurs in about 5% of pregnancies and is responsible for approximately 16% of all maternal deaths globally.[11] Pre-eclampsia also doubles the risk of death of the baby.[11] Usually there are no symptoms in pre-eclampsia and it is detected by routine screening. When symptoms of pre-eclampsia occur, the most common are headache, visual disturbance (often "flashing lights"), vomiting, epigastric pain, and edema (swelling). Pre-eclampsia can occasionally progress to a life-threatening condition called eclampsia. Eclampsia is a hypertensive emergency and has several serious complications. These complications include loss of ones sight swelling of the brain, seizures or convulsions, renal failure, pulmonary edema, and disseminated intravascular coagulation (a blood clotting disorder).[11][14]
Infants and children
Failure to thrive, seizures, irritability, lack of energy, and breathing difficulty[15] can be associated with hypertension in neonates and young infants. In older infants and children, hypertension can cause headache, unexplained irritability, fatigue, failure to thrive, blurred vision, nosebleeds, and facial paralysis.[6][15]
Complications
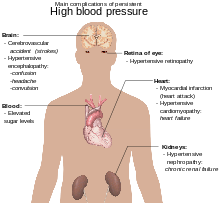
Hypertension is the most important preventable risk factor for premature death worldwide.[16] It increases the risk of ischemic heart disease[17] strokes,[11] peripheral vascular disease,[18] and other cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, aortic aneurysms, diffuse atherosclerosis, and pulmonary embolism.[11] Hypertension is also a risk factor for cognitive impairment, dementia, and chronic kidney disease.[11] Other complications include:
Cause
Primary hypertension
Primary (essential) hypertension is the most common form of hypertension, accounting for 90–95% of all cases of hypertension.[1] In almost all contemporary societies, blood pressure rises with aging and the risk of becoming hypertensive in later life is considerable.[20] Hypertension results from a complex interaction of genes and environmental factors. Numerous common genes with small effects on blood pressure have been identified[21] as well as some rare genes with large effects on blood pressure[22] but genetic basis of hypertension is still poorly understood. Several environmental factors influence blood pressure. Lifestyle factors that lower blood pressure include reduced dietary salt intake,[23] increased consumption of fruits and low-fat products (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH diet)). Exercise,[24] weight loss[25] and reduced alcohol intake also help lower blood pressure.[26] The possible role of other factors such as stress,[24] caffeine consumption,[27] and vitamin D deficiency[28] are less clear cut. Insulin resistance, which is common in obesity and is a component of syndrome X (or the metabolic syndrome), is also thought to contribute to hypertension.[29] Recent studies have also implicated events in early life (for example, low birth weight, maternal smoking, and lack of breast feeding) as risk factors for adult essential hypertension.[30] However, mechanisms linking these exposures to adult hypertension remain obscure.[30]
Secondary hypertension
Secondary hypertension results from an identifiable cause. Renal disease is the most common secondary cause of hypertension.[11] Hypertension can also be caused by endocrine conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, acromegaly, Conn's syndrome or hyperaldosteronism, hyperparathyroidism, and pheochromocytoma.[11][31] Other causes of secondary hypertension include obesity, sleep apnea, pregnancy, coarctation of the aorta, excessive licorice consumption and certain prescription medicines, herbal remedies, and illegal drugs.[11][32]
Pathophysiology

In most people with established essential (primary) hypertension, increased resistance to blood flow (total peripheral resistance) accounts for the high pressure while cardiac output remains normal.[33] There is evidence that some younger people with prehypertension or “borderline hypertension” have high cardiac output, an elevated heart rate, and normal peripheral resistance. This condition is called hyperkinetic borderline hypertension.[34] These individuals develop typical features of established essential hypertension in later life as their cardiac output falls and peripheral resistance rises with age.[34] Whether this pattern is typical of all people who ultimately develop hypertension is disputed.[35] Increased peripheral resistance in established hypertension is mainly attributable to structural narrowing of small arteries and arterioles.[36] Reduction in number or density of capillaries may also contribute to peripheral resistance.[37] Hypertension is also associated with decreased flexibility of peripheral veins,[38] which may increase return of blood to the heart, increase cardiac preload, and ultimately cause diastolic dysfunction. Whether increased active constriction of blood vessels plays a role in established essential hypertension is unclear.[39]
Pulse pressure (difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure) is frequently increased in older people with hypertension. This situation can involve systolic pressure that is abnormally high, but diastolic pressure may be normal or low. This condition is called isolated systolic hypertension.[40] High pulse pressure in elderly people with hypertension or isolated systolic hypertension is explained by increased arterial stiffness, which typically accompanies aging and may be exacerbated by high blood pressure.[41]
Many mechanisms have been proposed to account fo rise in resistance seen within arterial system in hypertension. Most evidence implicates one or both of these causes:
- Disturbances in renal salt and water handling, particularly abnormalities of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system[42]
- Abnormalities of sympathetic nervous system[43]
These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive and it is likely that both contribute to some extent in most cases of essential hypertension. It has also been suggested that endothelial dysfunction (dysfunction of lining of blood vessels) and vascular inflammation may also contribute to increased peripheral resistance and vascular damage in hypertension.[44][45]
Diagnosis
| System | Tests |
|---|---|
| Renal | Microscopic urinalysis, proteinuria, serum BUN (blood urea nitrogen) and/or creatinine |
| Endocrine | Serum sodium, potassium, calcium, TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone). |
| Metabolic | Fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, HDL and LDL cholesterol, triglycerides |
| Other | Hematocrit, electrocardiogram, and chest radiograph |
| Sources: Harrison's principles of internal medicine[46] others[47][48][49][50][51] | |
Hypertension is diagnosed when the patient has persistently high blood pressure. Traditionally,[3] diagnosis requires three separate sphygmomanometer measurements at one-month intervals.[52] Initial assessment of hypertensive patients includes a complete history and physical examination. With the availability of 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitors and home blood pressure machines, importance of avoiding an incorrect diagnosis of patients with white coat hypertension has led to a change in protocols. In the United Kingdom, current best practice is to follow up a single raised clinic reading with ambulatory measurement. Follow-up can also be done, but less ideally, with home blood pressure monitoring over the course of seven days.[3]
Once diagnosis of hypertension has been established, physicians attempt to identify the underlying cause based on risk factors and other symptoms, if present. Secondary hypertension is more common in preadolescent children and most cases are caused by renal disease. Primary or essential hypertension is more common in adolescents and has multiple risk factors, including obesity and a family history of hypertension.[53] Laboratory tests can also be performed to identify possible causes of secondary hypertension, and to determine whether hypertension caused damage to heart, eyes, and kidneys. Additional tests for diabetes and high cholesterol levels are performed because these conditions are risk factors for development of heart disease and may require treatment.[1]
Serum creatinine is measured to assess for the presence of kidney disease, which can be either the cause or the result of hypertension. Serum creatinine alone can overestimate glomerular filtration rate. Recent guidelines advocate the use of predictive equations such as the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula to estimate glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).[2] eGFR can also provide a baseline measurement of kidney function that can be used to monitor for side effects of certain antihypertensive drugs on kidney function. Testing of urine samples for protein is also used as a secondary indicator of kidney disease. Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) testing is done to check for evidence that the heart is under strain from high blood pressure. It can also show thickening of the heart muscle (left ventricular hypertrophy) or whether the heart has experienced a prior minor disturbance such as a silent heart attack. A chest X-ray or an echocardiogram can also be performed to look for signs of heart enlargement or damage to the heart.[11]
Prevention
The number of people who are hypertensive but do not realize it is substantial.[54] Measures that address to the whole population are required to reduce consequences of high blood pressure and minimise need for antihypertensive drug therapy. Lifestyle changes are recommended to lower blood pressure, before starting drug therapy. The 2004 British Hypertension Society guidelines[54] proposed the following lifestyle changes consistent with guidelines outlined by the US National High BP Education Program in 2002[55] for the primary prevention of hypertension are as follows:
- Maintain normal body weight (e.g., body mass index 20–25 kg/m2).
- Reduce dietary sodium intake to <100 mmol/ day (<6 g of sodium chloride or <2.4 g of sodium per day).
- Engage in regular aerobic physical activity such as brisk walking (≥30 min per day, most days of the week).
- Limit alcohol consumption to no more than 3 units/day in men and no more than 2 units/day in women.
- Consume a diet rich in fruit and vegetables (e.g., at least five portions per day).
Effective lifestyle modification may lower blood pressure as much an individual antihypertensive drug. Combinations of two or more lifestyle modifications can achieve even better results.[54]
Management
Lifestyle modifications
The first type of treatment for hypertension is identical to the recommended preventative lifestyle changes[56] and includes dietary changes[57] physical exercise, and weight loss. These changes have all been shown to significantly reduce blood pressure in people with hypertension.[58] If hypertension is high enough to justify immediate use of medications, lifestyle changes are still recommended. Different programs designed to reduce psychological stress such as biofeedback, relaxation, or meditation are advertised to reduce hypertension. However, scientific studies do not, in general, support their efficacy because the studies are generally of low quality.[59][60][61]
Dietary change such as a low-sodium diet is beneficial. A long-term (more than 4 weeks) low-sodium diet in Caucasians is effective in reducing blood pressure, both in people with hypertension and in people with normal blood pressure.[62] Also, the DASH diet, a diet rich in nuts, whole grains, fish, poultry, fruits, and vegetables, which is promoted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, lowers blood pressure. A major feature of the plan is limiting intake of sodium, although the diet is also rich in potassium, magnesium, calcium, and protein.[63]
Medications
Several classes of medications, collectively referred to as antihypertensive drugs, are currently available for treating hypertension. The person's cardiovascular risk (including risk of myocardial infarction and stroke) and blood pressure readings are considered when prescribing drugs.[64] If drug treatment is initiated, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Seventh Joint National Committee on High Blood Pressure (JNC-7)[2] recommends that the physician monitor for response to treatment and assess for any adverse reactions resulting from the medication. Reduction of blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and the risk of ischemic heart disease by 21%. Blood pressure reduction can also reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease.[65] The aim of treatment should be to reduce blood pressure to less than 140/90 mmHg for most individuals, and lower for those with diabetes or kidney disease. Some medical professionals recommend keeping levels below 120/80 mmHg.[64][66] If the blood pressure goal is not met, more treatment is needed.[67]
Guidelines on the choice of medication and how to best determine treatment for various subgroups have changed over time and differ between countries. Experts do not agree on the best medication.[68] The Cochrane collaboration, World Health Organization, and the United States guidelines support a low-dose thiazide-based diuretic as the preferred initial treatment.[68][69] UK guidelines emphasize calcium channel blockers (CCB) for people over the age of 55 or of African or Caribbean family origin. These guidelines recommend angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI)s as the preferred initial treatment for younger people.[70] In Japan, starting with any one of six classes of medications including: CCB, ACEI/ARB, thiazide diuretics, beta blockers, and alpha blockers is deemed reasonable. In Canada, all of these medications except alpha-blockers are recommended as possible first options.[68]
Drug combinations
Many people require more than one drug to control their hypertension. JNC7[2] and ESH-ESC guidelines[4] advocate starting treatment with two drugs when blood pressure is more than 20 mmHg above systolic or more than 10 mmHg above diastolic targets. Preferred combinations are renin–angiotensin system inhibitors and calcium channel blockers, or renin–angiotensin system inhibitors and diuretics.[71] Acceptable combinations include the following:
- Calcium channel blockers and diuretics
- Beta blockers and diuretics
- Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers and beta blockers
- Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers with either verapamil or diltiazem
Unacceptable combinations are as follows:
- Non-dihydropyridine calcium blockers (such as verapamil or diltiazem) and beta blockers
- Dual renin–angiotensin system blockade (e.g., angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor + angiotensin receptor blocker)
- Renin–angiotensin system blockers and beta blockers
- Beta blockers and anti-adrenergic drugs.[71]
Avoid combinations of an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist, a diuretic, and an NSAID (including selective COX-2 inhibitors and nonprescribed drugs such as ibuprofen) whenever possible due to a high risk of acute renal failure. The combination is known colloquially as a "triple whammy" in the Australian health literature.[56] Tablets containing fixed combinations of two classes of drugs are available. While they are convenient, they are best reserved for people who are established on the individual components.[72]
Elderly
Treating moderate to severe hypertension decreases death rates and cardiovascular side effects in people aged 60 and older.[73] In people over 80 years old treatment does not appear to significantly reduce total death rates but decreases risk of heart disease.[73] Recommended blood pressure goal is less than 140/90 mm Hg with thiazide diuretics being the preferred medication in America.[74] In the revised UK guidelines, calcium-channel blockers are the preferred treatment with target clinic readings of less than 150/90 mmHg, or less than 145/85 mmHg on ambulatory or home blood pressure monitoring.[70]
Resistant hypertension
Resistant hypertension is hypertension that remains above the blood pressure goal in spite of the use of three antihypertensive agents belonging to different antihypertensive drug classes all at once. Guidelines for treating resistant hypertension have been published in the UK[75] and the US.[76]
Likelihood
As of 2000, nearly one billion people or approximately 26% of the adult population of the world had hypertension.[77] It was common in both developed (333 million) and undeveloped (639 million) countries.[77] However, rates vary markedly in different regions with rates as low as 3.4% (men) and 6.8% (women) in rural India and as high as 68.9% (men) and 72.5% (women) in Poland.[78]
In 1995 it was estimated that 43 million people in the United States had hypertension or were taking antihypertensive medication. This figure represents almost 24% of the adult US population.[79] Rates of hypertension in the United States were increasing and reached 29% in 2004.[80][81] As of 2006 hypertension affects 76 million US adults (34% of the population) and African American adults have among the highest rates of hypertension in the world at 44%.[82] It is more common in native Americans and less common in whites and Mexican Americans. Rates increase with age, and are greater in the southeastern United States. Hypertension is more common in men comparing to women (though menopause tends to decrease this difference) and in those of low socioeconomic status.[1]
Children
Rates of high blood pressure in children is increasing.[83] Most childhood hypertension, particularly in preadolescents, is secondary to an underlying disorder. Aside from obesity, kidney disease is the most common (60–70%) cause of hypertension in children. Adolescents usually have primary or essential hypertension, which accounts for 85–95% of cases.[84]
History

Modern understanding of the cardiovascular system began with the work of physician William Harvey (1578–1657). Harvey described the circulation of blood in his book De motu cordis ("On the Motion of the Heart and Blood"). The English clergyman Stephen Hales made the first published measurement of blood pressure in 1733.[85][86] Descriptions of hypertension as a disease came from, among others, Thomas Young in 1808 and Richard Bright in 1836.[85] The first report of elevated blood pressure in a person without evidence of kidney disease was made by Frederick Akbar Mahomed (1849–1884).[87] However, hypertension as a clinical entity came into being in 1896 with the invention of the cuff-based sphygmomanometer by Scipione Riva-Rocci in 1896.[88] This invention allowed blood pressure to be measured in the clinic. In 1905, Nikolai Korotkoff improved the technique by describing the Korotkoff sounds that were heard when the artery was auscultated with a stethoscope while the sphygmomanometer cuff was deflated.[86]
Historically the treatment for what was called the "hard pulse disease" consisted of reducing the quantity of blood by blood letting or the application of leeches.[85] The Yellow Emperor of China, Cornelius Celsus, Galen, and Hippocrates advocated blood letting.[85] In the 19th and 20th centuries, before effective pharmacological treatment for hypertension became possible, three treatment modalities were used, all with numerous side effects. These modalities included strict sodium restriction (for example, the rice diet[85]), sympathectomy (surgical ablation of parts of sympathetic nervous system), and pyrogen therapy (injection of substances that caused a fever, indirectly reducing blood pressure).[85][89] The first chemical for hypertension, sodium thiocyanate, was used in 1900 but had many side effects and was unpopular.[85] Several other agents were developed after Second World War. The most popular and reasonably effective were tetramethylammonium chloride and its derivative hexamethonium, hydralazine, and reserpine (derived from the medicinal plant Rauwolfia serpentina). A major breakthrough was achieved with the discovery of the first well-tolerated available oral agents. The first was chlorothiazide, the first thiazide diuretic, which was developed from the antibiotic sulfanilamide and became available in 1958.[85][90] It increased salt excretion while preventing fluid accumulation. A randomized controlled trial that was sponsored by the Veterans Administration compared hydrochlorothiazide plus reserpine plus hydralazine versus placebo. The study was stopped early because those in a high blood pressure group who were not receiving treatment developed many more complications than treated patients and it was deemed unethical to withhold treatment from them. The study continued in people with lower blood pressures and showed that treatment, even in people with mild hypertension, cut the risk of cardiovascular death by more than half.[91] In 1975, the Lasker Special Public Health Award was given to the team that developed chlorothiazide.[89] Results of these studies prompted public health campaigns to increase public awareness of hypertension and promoted the measurement and treatment of high blood pressure. These measures appear to have contributed at least in part to the observed 50% fall in stroke and ischemic heart disease between 1972 and 1994.[89]
Society and culture
Awareness

The World Health Organization has identified hypertension, or high blood pressure, as the leading cause of cardiovascular mortality. The World Hypertension League (WHL), an umbrella organization of 85 national hypertension societies and leagues, recognized that more than 50% of the hypertensive persons worldwide are unaware of their condition.[92] To address this problem, the WHL initiated a global awareness campaign on hypertension in 2005 and dedicated May 17 of each year as World Hypertension Day (WHD). Over the past three years, more national societies have been engaging in WHD and have been innovative in their activities to get the message to the public. In 2007, there was record participation from 47 member countries of the WHL. During the week of WHD, all of these countries partnered with local governments, professional societies, nongovernmental organizations, and private industries to promote hypertension awareness through several media and public rallies. Using mass media such as the Internet and television, the message reached more than 250 million people. As the momentum picks up year after year, the WHL is confident that almost all of the estimated 1.5 billion people that are affected by elevated blood pressure can be reached.[93]
Economics
High blood pressure is the most common chronic medical problem prompting visits to primary health care providers in United States. The American Heart Association estimated the direct and indirect costs of high blood pressure at $76.6 billion in 2010.[82] In the United States, 80% of people with hypertension are aware of their condition and 71% take some antihypertensive medication. However, only 48% of people who are aware that they have hypertension adequately control the condition.[82] Inadequacies in diagnosis, treatment, or control of high blood pressure can compromise the management of hypertension.[94] Health care providers face many obstacles to achieving blood pressure control, including resistance to taking multiple medications to reach blood pressure goals. People also face challenges of adhering to medicine schedules and making lifestyle changes. Nonetheless, achievement of blood pressure goals is possible. Lowering blood pressure significantly reduces cost that is associated with advanced medical care.[95][96]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Carretero OA, Oparil S (2000). "Essential hypertension. Part I: Definition and etiology". Circulation. 101 (3): 329–35. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.101.3.329. PMID 10645931.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR; et al. (2003). "Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure". Hypertension. 42 (6): 1206–52. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2. PMID 14656957.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 National Clinical Guidance Centre (August 2011). "7 Diagnosis of Hypertension, 7.5 Link from evidence to recommendations". Hypertension (NICE CG 127) (PDF). National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. p. 102. Retrieved 2011-12-22. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "NICE127 full" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A; et al. (2007). "2007 ESH-ESC Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: ESH-ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension". J. Hypertens. 25 (9): 1751–62. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f0580f. PMID 17762635.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 5.0 5.1 Williams B, Poulter NR, Brown MJ; et al. (2004). "Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the fourth working party of the British Hypertension Society, 2004-BHS IV". J Hum Hypertens. 18 (3): 139–85. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001683. PMID 14973512.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Dionne JM, Abitbol CL, Flynn JT (2012). "Hypertension in infancy: diagnosis, management and outcome". Pediatr. Nephrol. 27 (1): 17–32. doi:10.1007/s00467-010-1755-z. PMID 21258818.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Din-Dzietham R, Liu Y, Bielo MV, Shamsa F (2007). "High blood pressure trends in children and adolescents in national surveys, 1963 to 2002". Circulation. 116 (13): 1488–96. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.683243. PMID 17846287.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents". Pediatrics. 114 (2 Suppl 4th Report): 555–76. 2004. PMID 15286277.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Fisher ND, Williams GH (2005). "Hypertensive vascular disease". In Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS; et al. (eds.). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (16th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1463–81. ISBN 0-07-139140-1.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|editor=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ↑ 10.0 10.1 Wong T, Mitchell P (2007). "The eye in hypertension". Lancet. 369 (9559): 425–35. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60198-6. PMID 17276782.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 11.10 11.11 11.12 11.13 11.14 11.15 11.16 11.17 O'Brien, Eoin; Beevers, D. G.; Lip, Gregory Y. H. (2007). ABC of hypertension. London: BMJ Books. ISBN 1-4051-3061-X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Papadopoulos DP, Mourouzis I, Thomopoulos C, Makris T, Papademetriou V (2010). "Hypertension crisis". Blood Press. 19 (6): 328–36. doi:10.3109/08037051.2010.488052. PMID 20504242.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 Marik PE, Varon J (2007). "Hypertensive crises: challenges and management". Chest. 131 (6): 1949–62. doi:10.1378/chest.06-2490. PMID 17565029.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Gibson, Paul (July 30, 2009). "Hypertension and Pregnancy". eMedicine Obstetrics and Gynecology. Medscape. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ↑ 15.0 15.1 Rodriguez-Cruz, Edwin (April 6, 2010). "Hypertension". eMedicine Pediatrics: Cardiac Disease and Critical Care Medicine. Medscape. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Global health risks: mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ↑ Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R (2002). "Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies". Lancet. 360 (9349): 1903–13. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8. PMID 12493255.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Singer DR, Kite A (2008). "Management of hypertension in peripheral arterial disease: does the choice of drugs matter?". European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 35 (6): 701–8. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2008.01.007. PMID 18375152.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Zeng C, Villar VA, Yu P, Zhou L, Jose PA (2009). "Reactive oxygen species and dopamine receptor function in essential hypertension". Clinical and Experimental Hypertension. 31 (2): 156–78. doi:10.1080/10641960802621283. PMID 19330604.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Vasan, RS (2002 Feb 27). "Residual lifetime risk for developing hypertension in middle-aged women and men: The Framingham Heart Study". JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 287 (8): 1003–10. PMID 11866648.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ The International Consortium for Blood Pressure Genome-Wide Association Studies. Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Nature 2011; 478: 103–109 doi:10.1038/nature10405
- ↑ Lifton, RP (2001 Feb 23). "Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension". Cell. 104 (4): 545–56. PMID 11239411.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ He, FJ (2009 Jun). "A comprehensive review on salt and health and current experience of worldwide salt reduction programmes". Journal of human hypertension. 23 (6): 363–84. PMID 19110538.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ 24.0 24.1 Dickinson HO, Mason JM, Nicolson DJ, Campbell F, Beyer FR, Cook JV, Williams B, Ford GA. Lifestyle interventions to reduce raised blood pressure: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens. 2006;24:215-33.
- ↑ Haslam DW, James WP (2005). "Obesity". Lancet. 366 (9492): 1197–209. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67483-1. PMID 16198769.
- ↑ Whelton PK, He J, Appel LJ, Cutler JA, Havas S, Kotchen TA; et al. (2002). "Primary prevention of hypertension:Clinical and public health advisory from The National High Blood Pressure Education Program". JAMA. 288 (15): 1882–8. doi:10.1001/jama.288.15.1882. PMID 12377087.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Mesas AE, Leon-Muñoz LM, Rodriguez-Artalejo F, Lopez-Garcia E. The effect of coffee on blood pressure and cardiovascular disease in hypertensive individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94:1113–26.
- ↑ Vaidya A, Forman JP (2010). "Vitamin D and hypertension: current evidence and future directions". Hypertension. 56 (5): 774–9. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.140160. PMID 20937970.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Sorof J, Daniels S (2002). "Obesity hypertension in children: a problem of epidemic proportions". Hypertension. 40 (4): 441–447. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000032940.33466.12. PMID 12364344. Retrieved 2009-06-03.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 30.0 30.1 Lawlor, DA (2005 May). "Early life determinants of adult blood pressure". Current opinion in nephrology and hypertension. 14 (3): 259–64. PMID 15821420.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ Dluhy RG, Williams GH. Endocrine hypertension. In: Wilson JD, Foster DW, Kronenberg HM, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders; 1998:729-49.
- ↑ Grossman E, Messerli FH (2012). "Drug-induced Hypertension: An Unappreciated Cause of Secondary Hypertension". Am. J. Med. 125 (1): 14–22. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.05.024. PMID 22195528.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Conway J (1984). "Hemodynamic aspects of essential hypertension in humans". Physiol. Rev. 64 (2): 617–60. PMID 6369352.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 34.0 34.1 Palatini P, Julius S (2009). "The role of cardiac autonomic function in hypertension and cardiovascular disease". Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 11 (3): 199–205. PMID 19442329.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Andersson OK, Lingman M, Himmelmann A, Sivertsson R, Widgren BR (2004). "Prediction of future hypertension by casual blood pressure or invasive hemodynamics? A 30-year follow-up study". Blood Press. 13 (6): 350–4. PMID 15771219.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Folkow B (1982). "Physiological aspects of primary hypertension". Physiol. Rev. 62 (2): 347–504. PMID 6461865.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Struijker Boudier HA, le Noble JL, Messing MW, Huijberts MS, le Noble FA, van Essen H (1992). "The microcirculation and hypertension". J Hypertens Suppl. 10 (7): S147–56. PMID 1291649.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Safar ME, London GM (1987). "Arterial and venous compliance in sustained essential hypertension". Hypertension. 10 (2): 133–9. PMID 3301662.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Schiffrin EL (1992). "Reactivity of small blood vessels in hypertension: relation with structural changes. State of the art lecture". Hypertension. 19 (2 Suppl): II1–9. PMID 1735561.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Chobanian AV (2007). "Clinical practice. Isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (8): 789–96. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp071137. PMID 17715411.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Zieman SJ, Melenovsky V, Kass DA (2005). "Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and therapy of arterial stiffness". Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25 (5): 932–43. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000160548.78317.29. PMID 15731494.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Navar LG (2010). "Counterpoint: Activation of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system is the dominant contributor to systemic hypertension". J. Appl. Physiol. 109 (6): 1998–2000, discussion 2015. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00182.2010a. PMC 3006411. PMID 21148349.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Esler M, Lambert E, Schlaich M (2010). "Point: Chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system is the dominant contributor to systemic hypertension". J. Appl. Physiol. 109 (6): 1996–8, discussion 2016. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00182.2010. PMID 20185633.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Versari D, Daghini E, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Taddei S (2009). "Endothelium-dependent contractions and endothelial dysfunction in human hypertension". Br. J. Pharmacol. 157 (4): 527–36. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00240.x. PMC 2707964. PMID 19630832.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Marchesi C, Paradis P, Schiffrin EL (2008). "Role of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular inflammation". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 29 (7): 367–74. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2008.05.003. PMID 18579222.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Loscalzo, Joseph; Fauci, Anthony S.; Braunwald, Eugene; Dennis L. Kasper; Hauser, Stephen L; Longo, Dan L. (2008). Harrison's principles of internal medicine. McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 0-07-147691-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Padwal RS; Hemmelgarn BR; Khan NA; et al. (2009). "The 2009 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part 1 – blood pressure measurement, diagnosis and assessment of risk". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 25 (5): 279–86. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(09)70491-X. PMC 2707176. PMID 19417858.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Padwal RJ; Hemmelgarn BR; Khan NA; et al. (2008). "The 2008 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part 1 – blood pressure measurement, diagnosis and assessment of risk". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 24 (6): 455–63. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(08)70619-6. PMC 2643189. PMID 18548142.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Padwal RS; Hemmelgarn BR; McAlister FA; et al. (2007). "The 2007 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part 1 – blood pressure measurement, diagnosis and assessment of risk". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 23 (7): 529–38. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(07)70797-3. PMC 2650756. PMID 17534459.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Hemmelgarn BR; McAlister FA; Grover S; et al. (2006). "The 2006 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part I – Blood pressure measurement, diagnosis and assessment of risk". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 22 (7): 573–81. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(06)70279-3. PMC 2560864. PMID 16755312.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Hemmelgarn BR; McAllister FA; Myers MG; et al. (2005). "The 2005 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 1- blood pressure measurement, diagnosis and assessment of risk". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 21 (8): 645–56. PMID 16003448.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ North of England Hypertension Guideline Development Group (1 August 2004). "Frequency of measurements". Essential hypertension (NICE CG18). National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. p. 53. Retrieved 2011-12-22.
- ↑ Luma GB, Spiotta RT (2006). "Hypertension in children and adolescents". Am Fam Physician. 73 (9): 1558–68. PMID 16719248.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 54.0 54.1 54.2 Williams, B (2004 Mar). "Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the fourth working party of the British Hypertension Society, 2004-BHS IV". Journal of human hypertension. 18 (3): 139–85. PMID 14973512.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ Whelton PK; et al. (2002). "Primary prevention of hypertension. Clinical and public health advisory from the National High Blood Pressure Education Program". JAMA. 288 (15): 1882–1888. doi:10.1001/jama.288.15.1882. PMID 12377087.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ↑ 56.0 56.1 "NPS Prescribing Practice Review 52: Treating hypertension". NPS Medicines Wise. September 1, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ↑ Siebenhofer, A (2011-09-07). Siebenhofer, Andrea (ed.). "Long-term effects of weight-reducing diets in hypertensive patients". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online). 9: CD008274. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008274.pub2. PMID 21901719.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ Blumenthal JA; Babyak MA; Hinderliter A; et al. (2010). "Effects of the DASH diet alone and in combination with exercise and weight loss on blood pressure and cardiovascular biomarkers in men and women with high blood pressure: the ENCORE study". Arch. Intern. Med. 170 (2): 126–35. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.470. PMID 20101007.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Greenhalgh J, Dickson R, Dundar Y (2009). "The effects of biofeedback for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review". Health Technol Assess. 13 (46): 1–104. doi:10.3310/hta13460. PMID 19822104.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|doi_brokendate=ignored (|doi-broken-date=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Rainforth MV, Schneider RH, Nidich SI, Gaylord-King C, Salerno JW, Anderson JW (2007). "Stress Reduction Programs in Patients with Elevated Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 9 (6): 520–8. doi:10.1007/s11906-007-0094-3. PMC 2268875. PMID 18350109.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Ospina MB; Bond K; Karkhaneh M; et al. (2007). "Meditation practices for health: state of the research". Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) (155): 1–263. PMID 17764203.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ He, FJ (2004). "Effect of longer-term modest salt reduction on blood pressure". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (3): CD004937. PMID 15266549.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Your Guide To Lowering Your Blood Pressure With DASH" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Nelson, Mark. "Drug treatment of elevated blood pressure". Australian Prescriber (33): 108–112. Retrieved August 11, 2010.
- ↑ Law M, Wald N, Morris J (2003). "Lowering blood pressure to prevent myocardial infarction and stroke: a new preventive strategy" (PDF). Health Technol Assess. 7 (31): 1–94. PMID 14604498.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Shaw, Gina (2009-03-07). "Prehypertension: Early-stage High Blood Pressure". WebMD. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- ↑ Eni C. Okonofua; Kit N. Simpson; Ammar Jesri; Shakaib U. Rehman; Valerie L. Durkalski; Brent M. Egan (January 23, 2006). "Therapeutic Inertia Is an Impediment to Achieving the Healthy People 2010 Blood Pressure Control Goals". Hypertension. 47 (2006, 47:345): 345–51. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000200702.76436.4b. PMID 16432045. Retrieved 2009-11-22.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 68.0 68.1 68.2 Klarenbach, SW (2010 May). "Identification of factors driving differences in cost effectiveness of first-line pharmacological therapy for uncomplicated hypertension". The Canadian journal of cardiology. 26 (5): e158-63. PMID 20485695.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ Wright JM, Musini VM (2009). Wright, James M (ed.). "First-line drugs for hypertension". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD001841. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001841.pub2. PMID 19588327.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 National Institute Clinical Excellence (August 2011). "1.5 Initiating and monitoring antihypertensive drug treatment, including blood pressure targets". GC127 Hypertension: Clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. Retrieved 2011-12-23.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Sever PS, Messerli FH (2011). "Hypertension management 2011: optimal combination therapy". Eur. Heart J. 32 (20): 2499–506. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr177. PMID 21697169.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ "2.5.5.1 Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors". British National Formulary. Vol. No. 62. September 2011.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|volume=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (help) - ↑ 73.0 73.1 Musini VM, Tejani AM, Bassett K, Wright JM (2009). Musini, Vijaya M (ed.). "Pharmacotherapy for hypertension in the elderly". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD000028. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000028.pub2. PMID 19821263.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Aronow WS, Fleg JL, Pepine CJ; et al. (2011). "ACCF/AHA 2011 expert consensus document on hypertension in the elderly: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus documents developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Neurology, American Geriatrics Society, American Society for Preventive Cardiology, American Society of Hypertension, American Society of Nephrology, Association of Black Cardiologists, and European Society of Hypertension". J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 57 (20): 2037–114. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.01.008. PMID 21524875.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "CG34 Hypertension - quick reference guide" (PDF). National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 28 June 2006. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ↑ Calhoun DA; Jones D; Textor S; et al. (2008). "Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research". Hypertension. 51 (6): 1403–19. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.189141. PMID 18391085.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 77.0 77.1 Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J (2005). "Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data". Lancet. 365 (9455): 217–23. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17741-1. PMID 15652604.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Whelton PK, He J (2004). "Worldwide prevalence of hypertension: a systematic review". J. Hypertens. 22 (1): 11–9. PMID 15106785.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Burt VL; Whelton P; Roccella EJ; et al. (1995). "Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population. Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1991". Hypertension. 25 (3): 305–13. PMID 7875754. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 80.0 80.1 Burt VL; Cutler JA; Higgins M; et al. (1995). "Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population. Data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991". Hypertension. 26 (1): 60–9. PMID 7607734. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ostchega Y, Dillon CF, Hughes JP, Carroll M, Yoon S (2007). "Trends in hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in older U.S. adults: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988 to 2004". Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 55 (7): 1056–65. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01215.x. PMID 17608879.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ 82.0 82.1 82.2 Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM; et al. (2010). "Heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association". Circulation. 121 (7): e46–e215. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192667. PMID 20019324.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Falkner B (2009). "Hypertension in children and adolescents: epidemiology and natural history". Pediatr. Nephrol. 25 (7): 1219–24. doi:10.1007/s00467-009-1200-3. PMC 2874036. PMID 19421783.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Luma GB, Spiotta RT (2006). "Hypertension in children and adolescents". Am Fam Physician. 73 (9): 1558–68. PMID 16719248.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 85.0 85.1 85.2 85.3 85.4 85.5 85.6 85.7 Esunge PM (1991). "From blood pressure to hypertension: the history of research". J R Soc Med. 84 (10): 621. PMC 1295564. PMID 1744849.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 86.0 86.1 Kotchen TA (2011). "Historical trends and milestones in hypertension research: a model of the process of translational research". Hypertension. 58 (4): 522–38. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.177766. PMID 21859967.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Swales JD, ed. (1995). Manual of hypertension. Oxford: Blackwell Science. pp. xiii. ISBN 0-86542-861-1.
- ↑ Postel-Vinay N, ed. (1996). A century of arterial hypertension 1896–1996. Chichester: Wiley. p. 213. ISBN 0-471-96788-2.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 Cite error: The named reference
Dustanwas used but no text was provided for refs named (see the help page). - ↑ Novello FC, Sprague JM (1957). "Benzothiadiazine dioxides as novel diuretics". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (8): 2028. doi:10.1021/ja01565a079.
- ↑ Freis ED (1974). "The Veterans Administration Cooperative Study on Antihypertensive Agents. Implications for Stroke Prevention" (PDF). Stroke. 5 (1): 76–77. doi:10.1161/01.STR.5.1.76. PMID 4811316.
- ↑ Chockalingam A (2007). "Impact of World Hypertension Day". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 23 (7): 517–9. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(07)70795-X. PMC 2650754. PMID 17534457.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Chockalingam A (2008). "World Hypertension Day and global awareness". Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 24 (6): 441–4. doi:10.1016/S0828-282X(08)70617-2. PMC 2643187. PMID 18548140.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Alcocer L, Cueto L (2008). "Hypertension, a health economics perspective". Therapeutic Advances in Cardiovascular Disease. 2 (3): 147–55. doi:10.1177/1753944708090572. PMID 19124418. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ William J. Elliott (2003). "The Economic Impact of Hypertension". The Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 5 (4): 3–13. doi:10.1111/j.1524-6175.2003.02463.x. PMID 12826765.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Coca A (2008). "Economic benefits of treating high-risk hypertension with angiotensin II receptor antagonists (blockers)". Clinical Drug Investigation. 28 (4): 211–20. doi:10.2165/00044011-200828040-00002. PMID 18345711.
