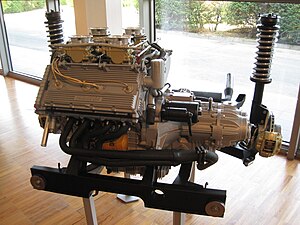
Lamborghini V8
| Lamborghini V8 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Lamborghini |
| Production | 1971-1988 |
| Layout | |
| Configuration | Naturally aspirated 90° V8 |
| Displacement | 2.0 L; 121.7 cu in (1,995 cc) 2.5 L; 150.3 cu in (2,463 cc) 3.0 L; 182.9 cu in (2,997 cc) 3.5 L; 212.7 cu in (3,485 cc) |
| Cylinder bore | 2.0: 77.4 mm (3.05 in) 2.5/3.0/3.5: 86 mm (3.39 in) |
| Piston stroke | 2.0/2.5: 53 mm (2.09 in) 3.0: 64.5 mm (2.54 in) 3.5: 75 mm (2.95 in) |
| Block material | Cast aluminium alloy |
| Head material | Cast aluminium alloy |
| Valvetrain | 2 valves per cylinder, 2.0/2.5/3.0: SOHC, 3.5: DOHC |
| Combustion | |
| Fuel system | Solex or Weber carburetors |
| Fuel type | Petrol/Gasoline |
| Oil system | Wet sump |
| Cooling system | Water-cooled |
| Output | |
| Power output | 2.0: 136 kW (185 PS; 182 bhp) @ 7,800 rpm 2.5: 164 kW (223 PS; 220 bhp) @ 7,500 rpm, then 190 kW (258 PS; 255 bhp) 3.0: 186 kW (253 PS; 249 bhp) @ 7,500 rpm, or 194 kW (264 PS; 260 bhp) @ 7,500 rpm, or 198 kW (269 PS; 266 bhp) @ 7,800 rpm 3.5: 190 kW (258 PS; 255 bhp) @ 7,000 rpm |
| Specific power | 2.0: 68.2 kW (92.7 PS; 91.5 bhp) per litre 3.5: 54.5 kW (74.1 PS; 73.1 bhp) per litre |
| Torque output | 3.0: 273 N⋅m (201 lb⋅ft) @ 5,750 rpm |
The Lamborghini V8 is a 90 degree V8 petrol engine. Lamborghini first made it in the 1970s for its cheaper cars.[1] It was the company's second internal combustion engine. The Lamborghini Urraco first used it in 1971.[2] The Lamborghini Silhouette used the engine in 1976-1977. The Lamborghini Jalpa also used it in 1982.[2] Gian Paolo Dallara first designed the engine.
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Lamborghini Urraco & the V8s Urraco, Bravo, Silhouette, Athon, Jalpa. Jean-Francois Marchet, Osprey autohistory, 1983
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Lamborghini Urraco, Silhouette & Jalpa". CarsFromItaly.net. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
