Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon
Lengadòc-Rosselhon (Occitan) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | |
| Dissolved | 2016-01-01 |
| Prefecture | Montpellier |
| Departments | |
| Government | |
| • President | Damien Alary (DVG) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 27,376 km2 (10,570 sq mi) |
| Population (2012-01-01) | |
| • Total | 2,700,266 |
| • Density | 99/km2 (260/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | FR-K |
| GDP (2012)[1] | Ranked 10th |
| Total | €63.9 billion (US$82.2 bn) |
| Per capita | €23,566 (US$30,311) |
| NUTS Region | FR8 |
| Website | laregion.fr |
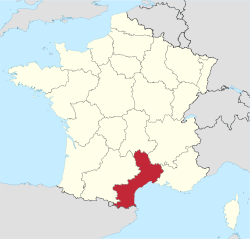
Languedoc-Roussillon (Occitan: Lengadòc-Rosselhon; Catalan: Llenguadoc-Rosselló) is a former administrative region of France. It is now part of the administrative region of Occitanie. It is the southernmost region of mainland France and borders to the south with Spain and Andorra.
The five departments in the region were Aude, Gard, Hérault, Lozère, and Pyrénées-Orientales.
Its capital was Montpellier, the largest city. In French, the name of the inhabitants of the region is Languedocien-Roussillonnais.
Etymology[change | change source]
The name of the province of Languedoc originates from the language spoken in southern France, langue d'oc, also known as Occitan, and Roussillon, an area in the South of present-day Languedoc-Roussillon.
Geography[change | change source]
The Languedoc-Roussillon region has an area of 27,376 km2 (10,570 sq mi). It bordered to the south with Spain and Andorra; to the east is the Mediterranean Sea (the Gulf of Lion). It also bordered four French regions: Midi-Pyrénées to the west, Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes to the north, and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur (PACA) to the northeast.
The highest point in Languedoc-Roussillon is Pic Carlit (42°34′11″N 01°55′55″E / 42.56972°N 1.93194°E) in the Pyrénées-Orientales department; it is 2,921 m (9,583 ft) high.[2]
Departments[change | change source]
The Languedoc-Roussillon region is formed by five departments:
| Département | Préfecture | ISO 3166-2 |
Population (2012)[3] |
Area (km²) |
Density (Inh./km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aude | Carcassonne | FR-11 | 362,339 | 6,139 | 59.0 |
| Gard | Nîmes | FR-30 | 725,618 | 5,853 | 124.0 |
| Hérault | Montpellier | FR-34 | 1,077,627 | 6,101 | 176.6 |
| Lozère | Mende | FR-48 | 76,889 | 5,167 | 14.9 |
| Pyrénées-Orientales | Perpignan | FR-66 | 457,793 | 4,116 | 111.2 |
Demographics[change | change source]
The Languedoc-Roussillon region has a population, in 2012, of 2,700,266,[4] for a population density of 98.6 inhabitants/km2.
The 10 most important cities in the region are:

| City | Population (2012)[3] |
Départment |
|---|---|---|
| Montpellier | 268456 | Hérault |
| Nîmes | 146,709 | Gard |
| Perpignan | 120,489 | Pyrénées-Orientales |
| Béziers | 72,970 | Hérault |
| Narbonne | 51,869 | Aude |
| Carcassonne | 47,068 | Aude |
| Sète | 44,558 | Hérault |
| Alès | 41,031 | Gard |
| Lunel | 25,405 | Hérault |
| Agde | 24,651 | Hérault |
Gallery[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ INSEE. "Produits intérieurs bruts régionaux et valeurs ajoutées régionales de 1990 à 2012". Retrieved 2014-03-04.
- ↑ "Le reliefs des Pyrénées-Orientales" (in French). A la découverte des Pyrénées Catalanes. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Populations légales 2012 des départements et des collectivités d'outre-mer" (in French). Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques - INSEE. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- ↑ "Populations légales 2012 des régions" (in French). Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques - INSEE. Retrieved 15 June 2015.






