Radon
Radon is a chemical element in the periodic table. It is element 86 on the periodic table and its symbol is Rn. It is an odorless, tasteless noble gas. It is quite radioactive and can decay very quickly. 27 isotopes of Radon are known today. The most stable of them has a half life of about 3.8 days.
Chemistry[change | change source]
Radon is a gas and is part of the group known as the noble gases. It does not react with other elements, so it is found pure. Radon is radioactive, meaning that it can give off harmful rays. Some people have high levels of radon in their houses, and this can be very dangerous. A lot of radon can get stuck in the basement of old houses, and so people end up breathing it in. It gets stuck in the lungs and has been known to cause cancer. There are groups that try to make sure there is no dangerous radon in houses.
It can occur naturally on the Earth but is a very small amount. As elements like Thorium and Uranium decay, some of that gets turned into Radon.
Radon can cause lung cancer and is the second most popular cause of lung cancer straight after smoking.
History[change | change source]
Radon was the fifth radioactive element to be discovered, in 1899 by Ernest Rutherford and Robert B. Owens at McGill University in Montreal, after uranium, thorium, radium, and polonium. In 1899, Pierre and Marie Curie saw that the gas given off by radium remained radioactive for a month. Later that year, Rutherford and Owens noticed different types of them when trying to measure radiation from thorium oxide.
Uses[change | change source]
It is sometimes used in radiation therapy. However, it is very dangerous to use.
| Radon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈreɪdɒn/ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | [222] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radon in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 18 (noble gases) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
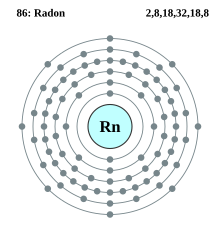
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | gas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 202 K (−71 °C, −96 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 211.5 K (−61.7 °C, −79.1 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at STP) | 9.73 g/L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at b.p.) | 4.4 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 377 K, 6.28 MPa[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 3.247 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 18.10 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 5R/2 = 20.786 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 0, +2, +6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 150 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 220 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | from decay | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 3.61×10−3 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | non-magnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 10043-92-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Ernest Rutherford and Robert B. Owens (1899) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | William Ramsay and Robert Whytlaw-Gray (1910) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of radon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related pages[change | change source]
References[change | change source]
- ↑ Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.122. ISBN 1439855110.
- ↑ Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


